第 328 场周赛
比赛链接
Date: 2023-01-15
A 数组元素和与数字和的绝对差
Python 快乐题
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:\(O(n)\)
- 空间复杂度:\(O(1)\)
B 子矩阵元素加 1
二维前缀和,容斥原理
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:\(O(n^2)\)
- 空间复杂度:\(O(n^2)\)
C 统计好子数组的数目
如果子数组 \([l, r]\) 是一个好子数组,那么对于所有的 \(r' \ge r\) , \([l, r']\) 都是好子数组。
所以,可以使用双指针(或者说是滑动窗口)来解决本题,对于每个 \(l\),求出最小的 \(r\) 使得 \([l, r]\) 是好子数组即可。过程中维护一个哈希表,记录区间内每种数字出现的次数,动态的维护 \((i, j), i<j, \textit{arr}[i]=\textit{arr}[j]\) 的个数。
| class Solution {
public:
using ll = long long;
long long countGood(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
ll res = 0;
ll sum = 0;
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
auto update = [&](int x, int cnt) {
sum -= 1ll * mp[x] * (mp[x] - 1) / 2;
mp[x] += cnt;
sum += 1ll * mp[x] * (mp[x] - 1) / 2;
};
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
while (j < nums.size() && sum < k) {
update(nums[j], 1);
j++;
}
if (sum >= k) {
res += nums.size() - j + 1;
}
update(nums[i], -1);
}
return res;
}
};
|
| class Solution:
def isItPossible(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> bool:
h1, h2 = Counter(word1), Counter(word2)
l1, l2 = len(h1), len(h2)
for x in h1:
for y in h2:
if x == y:
if l1 == l2:
return True
continue
# 计算交换操作之后的种类数
nl1 = l1 - 1 if h1[x] == 1 else l1
nl2 = l2 - 1 if h2[y] == 1 else l2
nl1 = nl1 + 1 if h1[y] == 0 else nl1
nl2 = nl2 + 1 if h2[x] == 0 else nl2
if nl1 == nl2:
return True
return False
|
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:\(O(n)\)
- 空间复杂度:\(O(n)\)
D 最大价值和与最小价值和的差值
首先,树中最远的两点距离被称为树的直径。我们可以用两次 BFS 来求出它。
- 首先随便选一个点(比如 \(0\))进行 BFS,结束后找到距离起点最远的点,把它设为 \(s\)。
- 然后从 \(s\) 开始 BFS,结束后找到距离 \(s\) 最远的点,把它设为 \(t\)。
此时,\(s\) 到 \(t\) 的距离就是树的直径,是整个树中两点配对距离最远的一对点。
但是最终的答案并不一定是以 \(s\) 或者 \(t\) 为根。例如下图中,\(1\) 到 \(5\) 是直径,但是答案是 \(7\) 到 \(5\)。
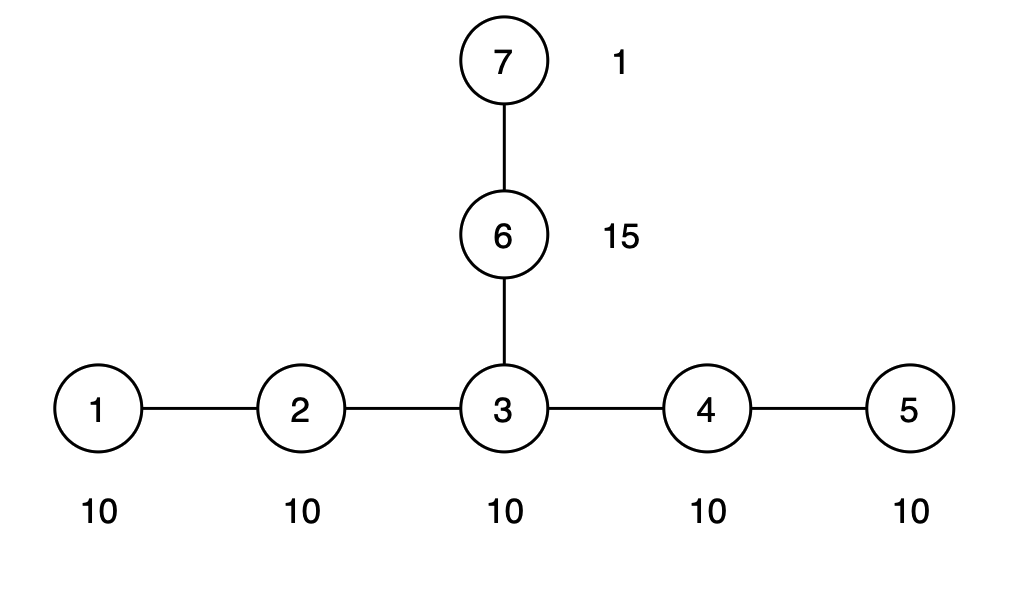
所以,我们应该求出从 \(s\) 以及从 \(t\) 出发到达所有点的距离。然后遍历所有点,枚举以它为根时的答案。这样做的正确性在于,在树中距离每个点最远的点不是 \(s\) 就一定是 \(t\)。
| class Solution {
public:
using ll = long long;
using PII = pair<int, int>;
long long maxOutput(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& price) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto v : edges) {
g[v[0]].push_back(v[1]);
g[v[1]].push_back(v[0]);
}
vector<ll> ds(n), dt(n);
auto bfs = [&](int s, vector<ll>& d) -> int {
vector<ll> v(n);
d[s] = price[s];
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
v[s] = 1;
int rt = -1;
while (q.size()) {
auto x = q.front(); q.pop();
if (rt == -1 || d[rt] < d[x]) {
rt = x;
}
for (auto y : g[x]) {
if (v[y]) continue;
d[y] = d[x] + price[y];
q.push(y);
v[y] = 1;
}
}
return rt;
};
auto s = bfs(0, ds);
auto t = bfs(s, ds);
bfs(t, dt);
ll res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = max(res, 1ll * max(ds[i], dt[i]) - 1ll * price[i]);
}
return res;
}
};
|
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:\(O(n)\)
- 空间复杂度:\(O(n)\)
本站总访问量 Loading 次
本站总访客数 Loading 人
